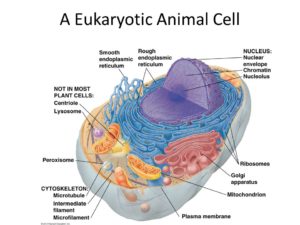
All organisms are made of cells
– The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live (reproduce)
– Cell structure is correlated with cellular function.
– All cells are related by their descent from earlier cells.
Viruses are considered not to live because their reproduction depends on other organisms.
How do we study cells?
Normally, cells are too small to be seen by eye so we must use microscopes and other techniques like biochemistry to study them
Light microscope : the best magnification 1/1000
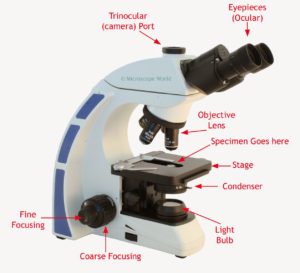
The quality of the image depends on 3 things
1) Magnification : rates of an object’s image size to its real size
2) Resolution : basically it means the clarity of the image (the minimum size visible)
3) Contrast
Electron microscopy
– Two basic types of electron microscopes are used to study subcellular structures
1) Scanning electron microscopes focus a beam of electrons outs the surface of a specimen, providing images that look there dimensional.
2) Transmission electron microscopes :
Focus a beam of electrons through a specimen (TEMS), this kind of electron microscope is used to study the internal structure of cells.
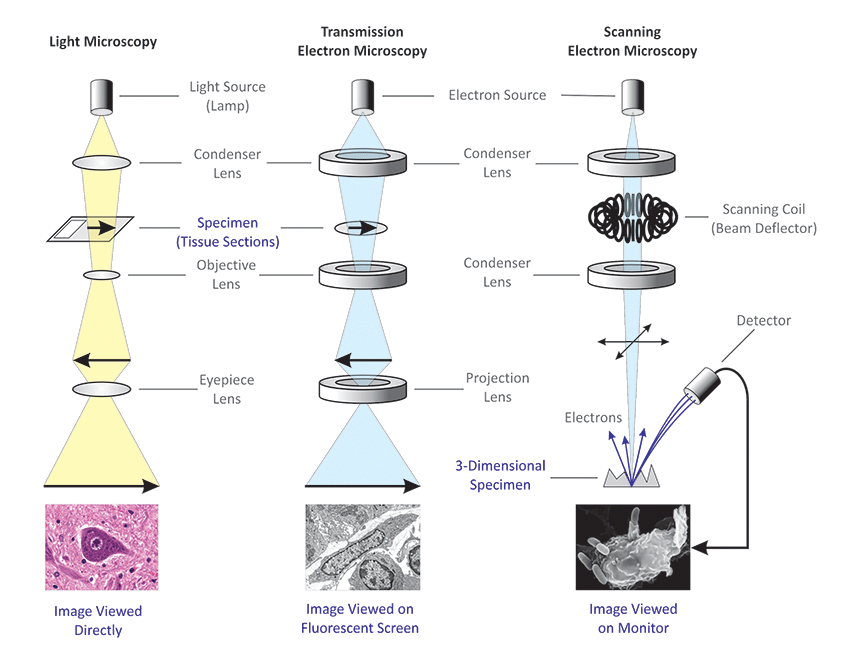
Example of scanning and transmission electron microscopy.


Cell fractionation
– Cell fractionation : one takes cells apart and separate the major organelles from one anther
– Ultra centrifugation fractionate cells into their component parts.
– Cell fractionation enables scientists to determine the functions of organs
– Biochemistry and cytology help correlate cell function with structure.
Comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic
– Basic features of all cells
.) Plasma membrane
.) Semifluid substance cells cytosol
.) Chromosomes (carry genes)
.) Ribosomes (make proteins)
– The structural and functional unit of every organism is one of two types of cells : prokaryotic or eukaryotic
– Only organisms of the domains bacteria and arches
– consist of prokaryotic cells
– fungi, animals and plants all consist of eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells
– No nucleus
– DNA is an unbound region called the nucleoid
– No membrane bound organ cells
– Cytoplasm bound by the plasma membrane

– DNA is in a nucleus that is bounded by a membranous nuclear envelope
– Cytoplasm in the region between the plasma membrane and nucleus
– Eukaryotic cells are generally much larger than prokaryotic cells